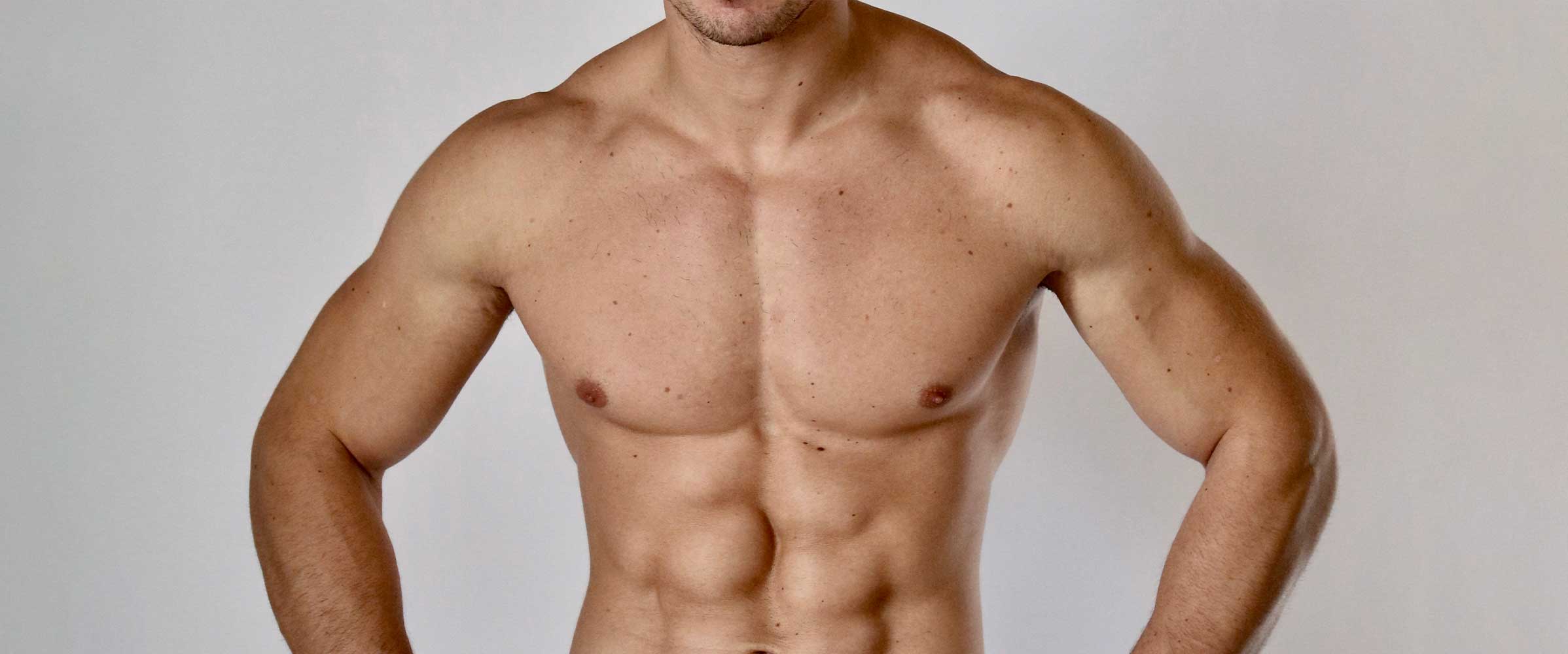
Gynecomastia is the enlargement of the breast tissue in men, similar to the breast tissue of the blood. Breast enlargement in men is not always a sign of disease. Hormonal irregularities, obesity, aging, some drugs used and some tumors can cause gynecomastia during adolescence. The most common causes of gynecomastia are hormonal changes in adolescence and breast enlargement due to aging. Gynecomastia can lead to a decrease in self-confidence and social and psychological problems in men, especially in adolescents.
Gynecomastia is divided into three types. The first type is mostly seen in adolescence and there is an increase in real breast tissue. The second type of gynecomastia is usually seen in older people and obese people. In this type, an increase in the adipose tissue in the breast is observed. The third type of gynecomastia is called the mixed type. In this type of gynecomastia, there is an increase in both breast tissue and adipose tissue. Treatment methods vary according to the types of gynecomastia. The type of gynecomastia can be determined by preoperative ultrasonography and physical examination.
Anesthesia
General
Operation
60-120 min.
Recovery Time
1-2 week
Final Conclusion
3-6 Months
Pain
Minimal
Since gynecomastia complaints that occur during adolescence may be due to hormonal changes, at least 2 years should be waited for surgical intervention. It would be appropriate to show severe gynecomastia cases seen in this period to an endocrinology specialist. Gynecomastias that do not regress within 2 years after puberty can be operated.
In obese people and gynecomastia that occurs in later ages, surgery can be performed after the necessary controls are made.
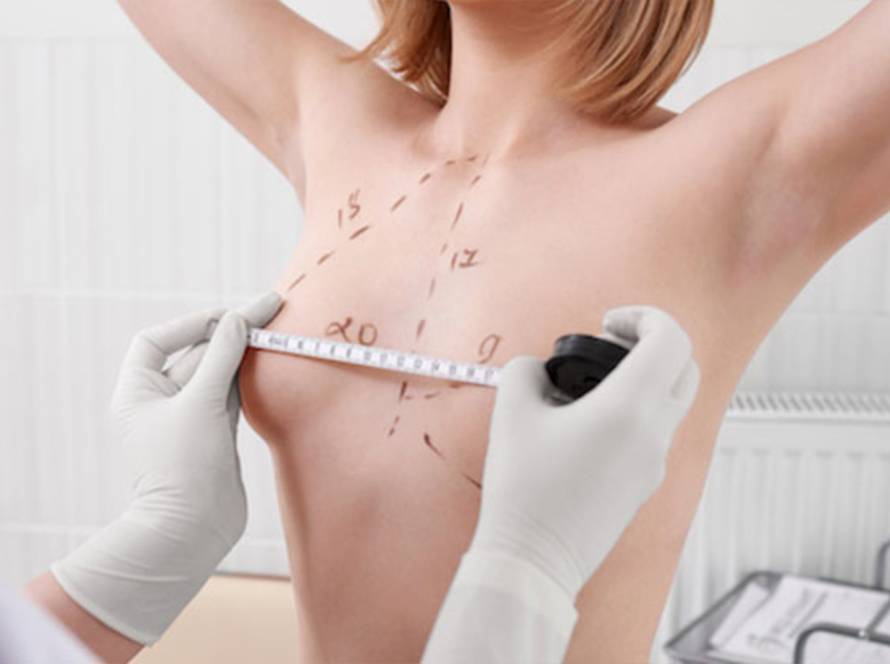
During the pre-operative interview, a physical examination is performed. Evaluation is made with ultrasonography and, if necessary, other examinations. The type of gynecomastia is determined and a treatment plan is created. Detailed information about the operation process and after is given.
Aspirin and derivative blood thinners are discontinued one week before the operation. If there is a blood thinner that must be taken, the doctor should be informed.
Although smoking does not prevent surgery, it is recommended to stop before surgery.
When coming to the hospital on the day of surgery, comfortable clothes should be preferred and any jewelry should be removed. At least 6 hours before the operation, nothing should be eaten and nothing should be drunk, including water.
You should be in the hospital at least two hours before the operation.
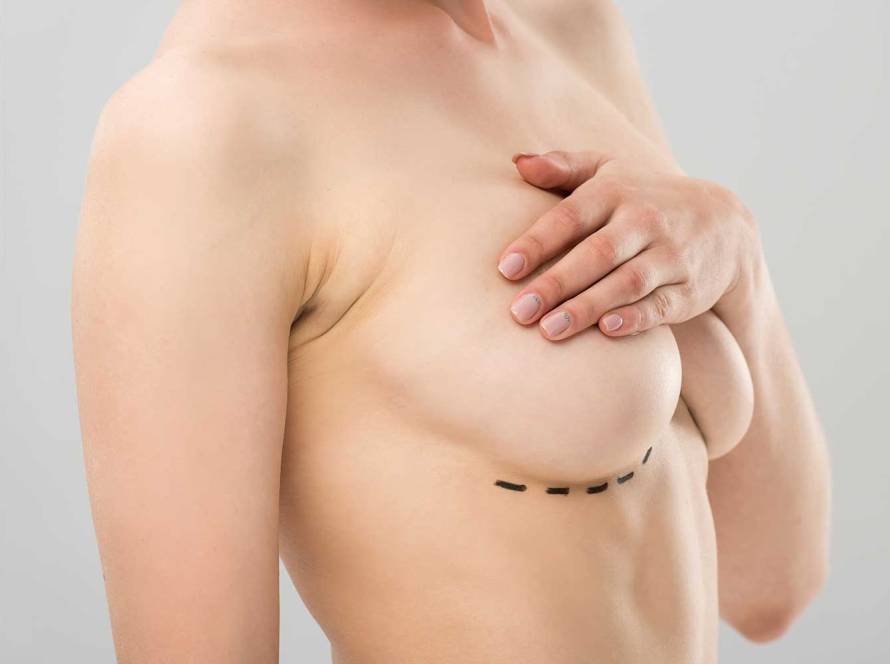
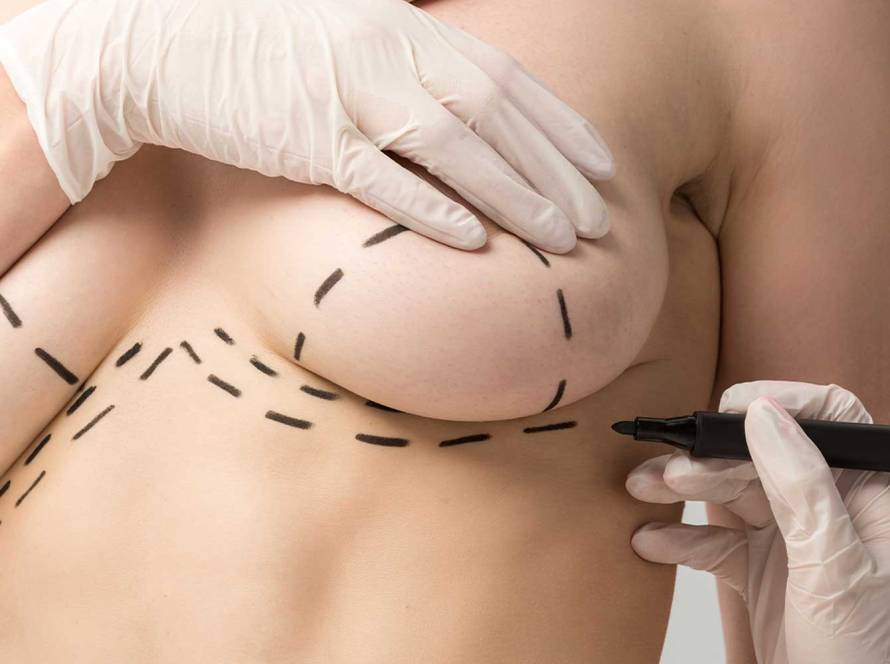
The surgical technique may vary depending on the type and size of gynecomastia. If there is no excess skin in mixed type and lipomatous type gynecomastia, liposuction is usually sufficient. In type 1 gynecomastia where the increase in breast tissue is prominent, the breast tissue can be removed with a semicircular incision made on the side of the dark part of the breast called the areola.
In larger gynecomastia with excess skin, the skin should be removed alongside liposuction and breast tissue. In people whose skin is removed, the scars can be lollipop-shaped or inverted T-shaped.
Depending on the size of the gynecomastia, it can be performed with local, general or sedation anesthesia.
Depending on the operation to be performed, the duration varies, but averages between 1-3 hours.
The patient is dressed in a corset after the surgery. Eating and drinking starts 3-4 hours after the operation and the patient can stand up and walk. The patient can be discharged on the same day or after one day of hospitalization.
It is normal to have swelling and bruising in the surgical area after the gynecomastia operation. Bruises usually disappear up to 10 days, swelling after 3 weeks. The final shape takes 3-6 months to form.
The patient can take a bath after the 3rd day after the operation and returns to his normal life within 3-4 days.
Exercises such as walking, which do not tire the patient much, can be started after the 10th day. More active exercises such as running, swimming and lifting weights can be started from the 2nd month.